Overview
The article delineates four crucial steps for safeguarding software as intellectual property:
- Registering copyrights and patents
- Utilizing non-disclosure agreements
- Implementing technical protections
- Establishing clear legal agreements
These strategies are not merely recommendations; they are vital mechanisms for protecting innovations from infringement and unauthorized use. By providing robust legal backing and practical measures, they empower creators to maintain control over their software developments in a competitive market.
How well are you protecting your intellectual property? Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance your position against potential threats.
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, the safeguarding of software intellectual property (IP) is an imperative concern for both developers and businesses.
With the rapid advancements in technology, grasping the intricacies of software IP is crucial for protecting creative works from unauthorized use and infringement. This article examines the essential aspects of software IP, focusing on vital protections such as:
- copyrights
- patents
- trademarks
- trade secrets
It underscores effective strategies for defending these innovations, the significance of legal agreements, and the impact of advanced technology in enhancing IP management. As the stakes escalate, navigating the complexities of software IP transcends mere legal necessity; it emerges as a strategic imperative for achieving long-term success in the competitive tech arena.
Define Software Intellectual Property
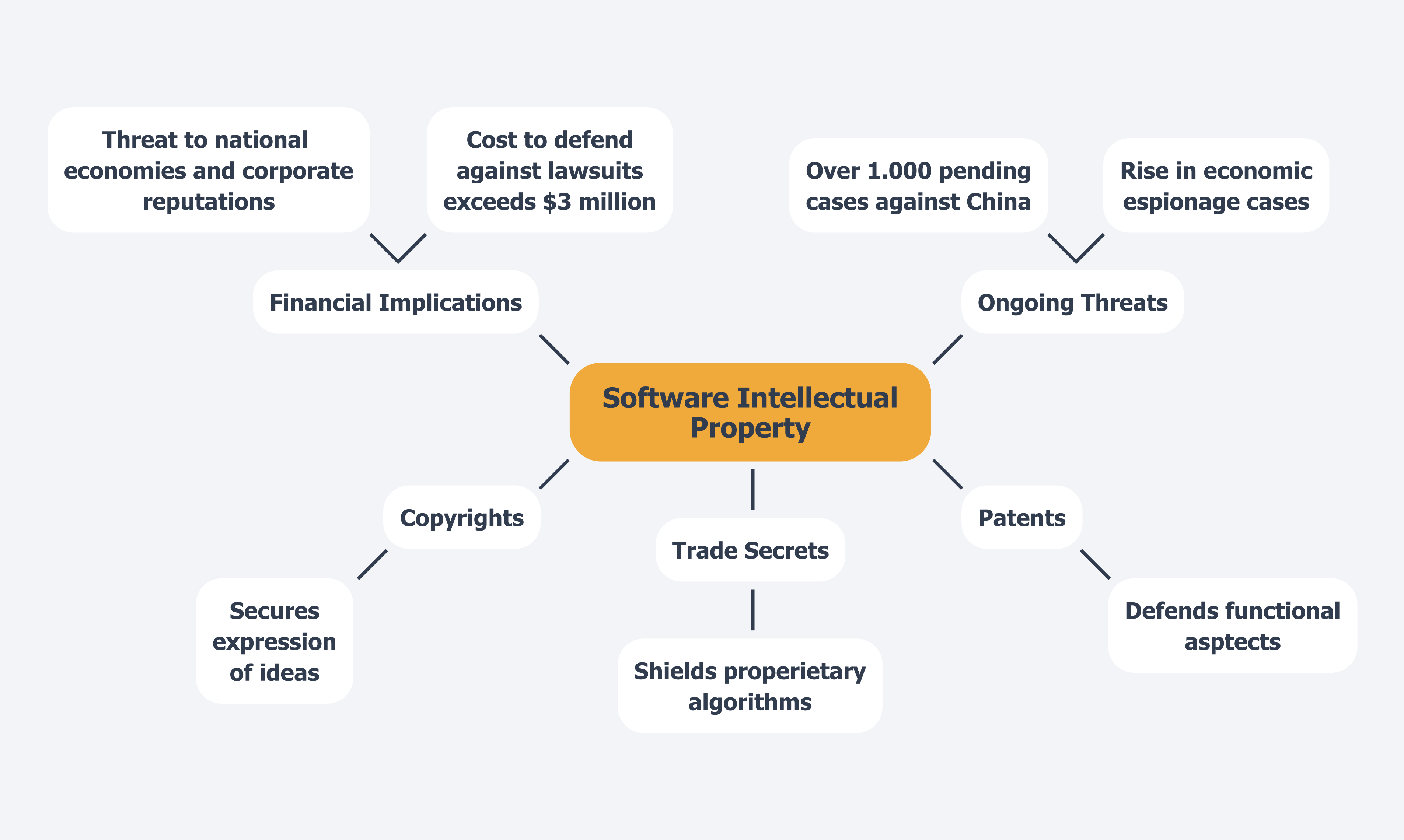
Intellectual property (IP) encompasses the legal rights that protect innovative creations within technology development, including original and non-obvious computer code, programs, applications, and algorithms. As we approach 2025, understanding software as intellectual property is increasingly vital because it encompasses various types of protections:
- Copyrights secure the expression of ideas.
- Patents defend the functional aspects of software.
- Trade secrets shield proprietary algorithms and processes.
The implications of these protections are significant; for instance, the costs to defend against IP infringement lawsuits can exceed $3 million, highlighting the financial stakes involved in safeguarding innovations. Moreover, with over 1,000 pending cases against China related to IP theft, the threat of infringement is substantial, affecting national economies, corporate reputations, and even public safety.
This report, a collaboration between the OECD and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission, underscores the persistent threat to US intellectual assets and the urgent need for diligent enforcement measures. By clearly defining software as intellectual property, developers and creators can more effectively navigate the complexities of legal protections, ensuring their innovations are secured against unauthorized use and economic espionage.
Explore Types of Intellectual Property Protections
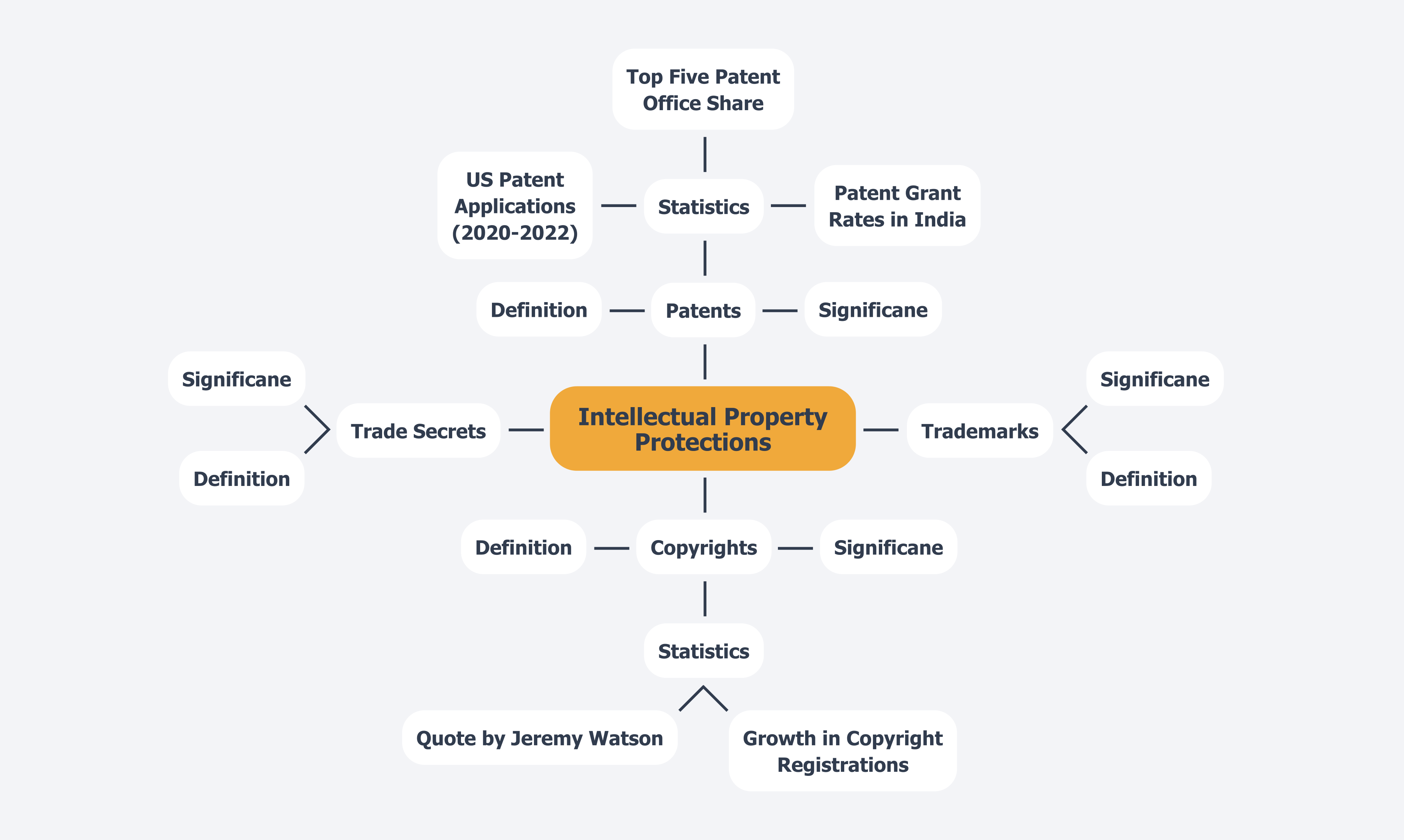
Four primary types of intellectual property protections are essential for safeguarding software:
- Copyrights: These safeguards automatically encompass the original code and documentation of applications, granting creators exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, and alter their work. The substantial growth in copyright registrations for applications in recent years indicates a rising acknowledgment of the significance of these protections in the digital realm. As noted by Jeremy Watson from the University of Minnesota, “We hope that the availability of these data can facilitate progress on copyright research to parallel the broader intellectual property literature that has blossomed since patent data became widely available.”
- Patents: Patents protect inventions and processes that are novel and non-obvious. Software can be patented if it meets specific criteria, such as being tied to a technical solution. In 2024, the quantity of technology patents submitted reached a significant peak, highlighting the trend of innovation in this sector. Notably, the US filed 13.8% of all published applications in computer technology between 2020 and 2022, showcasing its competitive landscape. Furthermore, the combined share of the top five patent offices has increased from 81% in 2013 to 85% in 2023, indicating a global trend in patent filings.
- Trademarks: Trademarks protect brand names, logos, and slogans linked to applications, ensuring that consumers can recognize the origin of a product. This safeguard is crucial for maintaining brand integrity and consumer trust in a competitive market.
- Trade Secrets: Trade secrets protect confidential business information that provides a competitive edge, including algorithms, formulas, and processes that are not publicly disclosed. The strategic management of trade secrets is essential for technology firms aiming to preserve their innovative advantages. For instance, in 2023, the IP office of India granted patents for approximately 81.4% of applications processed, showcasing a high grant rate compared to other major patent offices, which illustrates the efficiency of patent examination processes in different jurisdictions.
By comprehending these safeguards, developers can strategically choose the most effective techniques to secure their software as intellectual property, thus promoting innovation and ensuring long-term success in the marketplace.
Implement Strategies for Protecting Software IP
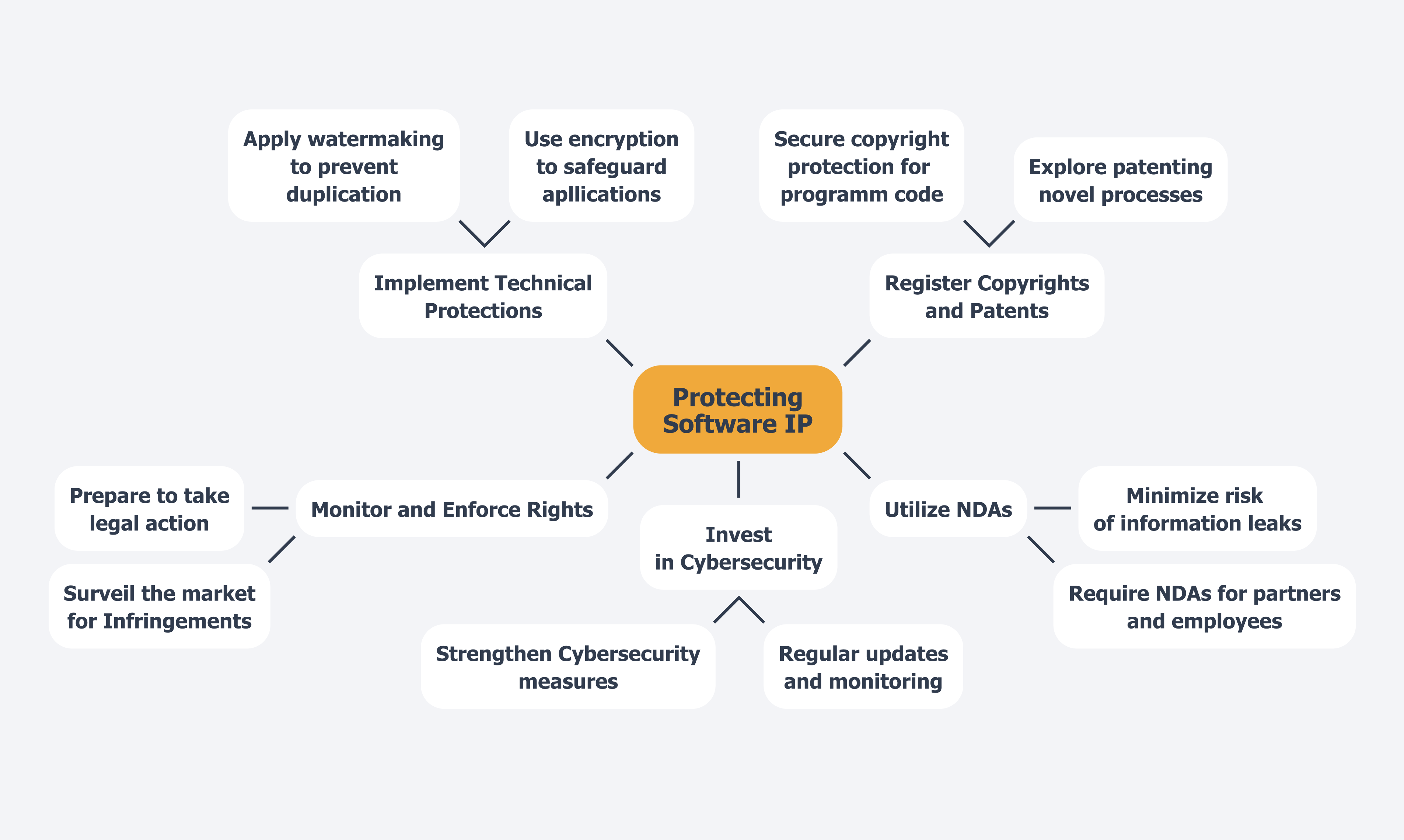
To effectively safeguard software intellectual property (IP), consider implementing the following strategies:
- Register Copyrights and Patents: Secure copyright protection for your program code and explore patenting any novel processes or functionalities. This legal recognition is crucial for asserting your rights and deterring infringement.
- Utilize Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): When collaborating with potential partners or employees, require them to sign NDAs. These agreements legally obligate parties to confidentiality, greatly minimizing the risk of information leaks and unauthorized use of your application.
- Implement Technical Protections: Employ advanced technical measures such as encryption and watermarking to safeguard your applications from unauthorized access and duplication. These tools act as a first line of defense against IP theft.
- Invest in Cybersecurity: Strengthening your cybersecurity measures is essential for protecting business assets. This includes regular updates and monitoring to safeguard against potential breaches.
- Monitor and Enforce Your Rights: Regularly surveil the market for potential infringements. Be prepared to take action, which may include sending cease-and-desist letters or pursuing litigation. Proactive enforcement is essential to maintaining the integrity of your IP.
In 2025, the landscape of safeguarding software as intellectual property continues to evolve, with statistics indicating that the theft of software as intellectual property remains a significant concern. For instance, the Apple vs. Samsung lawsuit, which lasted for seven years, resulted in Apple being awarded $539 million, highlighting the financial implications of IP theft. Companies that effectively utilize NDAs and technical safeguards are better positioned to defend their innovations. As Kary Oberbrunner, a former Forbes Councils Member, stated, “Protecting your ideas is not just a matter of personal interest; it is crucial for fostering a thriving and competitive economic environment.” Furthermore, digital forensics has emerged as a vital tool in recovering stolen information and deterring further misappropriation of trade secrets, as illustrated in the case study titled “The Role of Digital Forensics in IP Theft Recovery.” This showcases the importance of a multifaceted approach to IP protection.
Establish Legal Agreements and Documentation
Establishing clear legal contracts is essential for safeguarding software as intellectual property. The key agreements include:
- Software Development Contracts: These contracts delineate the terms of development, specifying ownership of the resulting IP, payment structures, and timelines. They are vital in preventing disputes over ownership and ensuring that all parties are aligned on expectations. Furthermore, companies that conduct frequent evaluations of their programs can enhance user satisfaction rates by over 40%, emphasizing the significance of establishing clear arrangements to enable efficient program management. Leveraging iPNOTE’s AI-driven features can further enhance the management of these contracts, ensuring timely execution and compliance while permitting task delegation and workflow oversight.
- Licensing Agreements: These documents outline the parameters under which others can utilize your programs, including any restrictions and associated fees. Well-organized licensing contracts can greatly diminish the chances of conflicts, which data indicate occur often in licensing scenarios. iPNOTE allows for easy integration of service providers, enabling efficient tracking and management of licensing terms, thus enhancing workflow optimization.
- Employment Contracts: It is crucial that these contracts clarify that any software developed by employees during their tenure is owned by the company. This protects the organization’s interests and reinforces the understanding of IP ownership among staff. iPNOTE’s platform can help manage these contracts effectively, ensuring that all parties are aware of their obligations and facilitating communication through its integrated chat feature.
- Confidentiality Contracts: These contracts safeguard sensitive information shared with third parties, ensuring that proprietary data remains protected. Given that 43% of small firms experience data breaches, robust confidentiality measures are increasingly important. The urgency of implementing such measures is emphasized by the need for organizations to safeguard their intellectual assets in a landscape where data breaches are common. iPNOTE’s dedication to data security, encompassing privacy policies and role-based access control, strengthens the safeguarding of these contracts.
By formalizing these contracts and utilizing iPNOTE’s comprehensive services, software developers can mitigate risks and clarify ownership rights, which is essential for maintaining control over their software as intellectual property. The legal landscape is evolving, and as hybrid work models become more prevalent, the need for secure, centralized contract repositories is more critical than ever. The case study titled “Technological Innovations Driving Progress in the Legal Sector” illustrates how advancements in technology, such as those offered by iPNOTE, can streamline the management of these legal agreements, ultimately leading to reduced document review times and improved client satisfaction.
Conclusion
Safeguarding software intellectual property (IP) represents a multifaceted endeavor that necessitates a focus on various protective measures, including copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. Each type of protection is essential in securing innovations from unauthorized use, enabling developers and businesses to sustain their competitive edge in an ever-evolving digital landscape. As discussed in the article, comprehending and effectively implementing these protections is vital, particularly as the financial stakes associated with IP infringement continue to escalate.
To protect software IP, strategies such as registering copyrights and patents, utilizing non-disclosure agreements, and investing in cybersecurity are critical steps that can strengthen a company’s defenses against potential threats. Furthermore, establishing clear legal agreements can minimize disputes and clarify ownership rights, which is increasingly crucial in a landscape rife with data breaches and IP theft. The integration of advanced technologies, such as those offered by platforms like iPNOTE, can further streamline these processes, enhancing the management of legal agreements and ensuring compliance.
Ultimately, the proactive protection of software intellectual property is not merely a legal obligation; it is a strategic imperative that can significantly influence long-term success. As the digital world becomes more intricate, the importance of safeguarding innovations grows increasingly critical for both developers and businesses. By adopting comprehensive protection strategies and fostering a culture of IP awareness, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of software IP, paving the way for sustained innovation and market leadership.
Protect Your Innovations with Smart IP Management! Start now with iPNOTE and secure your competitive edge in the digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is intellectual property (IP) in the context of technology development?
Intellectual property (IP) refers to the legal rights that protect innovative creations within technology development, including original and non-obvious computer code, programs, applications, and algorithms.
Why is understanding software as intellectual property important as we approach 2025?
Understanding software as intellectual property is increasingly vital because it encompasses various types of protections that help secure innovations against unauthorized use and economic espionage.
What are the different types of protections for software as intellectual property?
The different types of protections include: 1. Copyrights, which secure the expression of ideas. 2. Patents, which defend the functional aspects of software. 3. Trade secrets, which shield proprietary algorithms and processes.
What are the financial implications of defending against IP infringement lawsuits?
The costs to defend against IP infringement lawsuits can exceed $3 million, highlighting the significant financial stakes involved in safeguarding innovations.
What is the current situation regarding IP theft cases against China?
There are over 1,000 pending cases against China related to IP theft, indicating a substantial threat of infringement that affects national economies, corporate reputations, and public safety.
What does the report by the OECD and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission emphasize?
The report underscores the persistent threat to US intellectual assets and the urgent need for diligent enforcement measures to protect these assets.
How can clearly defining software as intellectual property benefit developers and creators?
By clearly defining software as intellectual property, developers and creators can more effectively navigate the complexities of legal protections, ensuring their innovations are secured against unauthorized use and economic espionage.