Introduction: A Clear Path to Trademark Registration in Thailand
Trademark Registration Process in Thailand: Overview
Budget: What Trademark Registration Costs in Thailand
Timeline: How Long Trademark Registration Takes in Thailand
1. Introduction: A Clear Path to Trademark Registration in Thailand
Registering a trademark in Thailand can feel challenging for businesses entering the Thai market for the first time. Local requirements, Thai-language specifics, single-class applications, and unique examination practices often make applicants worried about missing a detail, choosing the wrong class, or receiving a refusal.
This guide provides a simple, structured, step-by-step path — from the initial trademark search to obtaining your registration certificate — and explains how you can complete the entire process smoothly with the support of verified local attorneys through a unified platform, without confusion, delays, or unexpected costs.
Whether you’re launching a new product in Thailand or protecting an existing brand portfolio, understanding the country’s rules will help avoid refusals, delays, and unnecessary expenses.
What Can Be Registered as a Trademark in Thailand?
Thailand allows protection for a wide range of brand identifiers under the Thai Trademark Act B.E. 2534 (1991) (as amended).
You can register:
- Word marks (including English, Thai, and other languages)
- Logos and graphic elements
- Combination marks
- 3D marks
- Color or color combinations (if distinctive)
- Sound marks (allowed since 2017)
- Any combination of the above
The essential requirement is distinctiveness — the mark must be capable of distinguishing your goods or services from those of others. Thailand applies a stricter interpretation of distinctiveness compared to many Western jurisdictions.
Grounds for Refusal in Thailand: What Can Cause Problems?
Thailand’s Department of Intellectual Property (DIP) may refuse a trademark if:
Absolute Grounds (Inherent Issues)
- The mark is generic, descriptive, or indicates quality, purpose, price, or geographical origin.
- The mark is contrary to public order, morality, or public policy.
- The mark contains national flags, royal symbols, or official emblems without permission.
- Marks that directly reference Thai royal institutions are rejected automatically.
Relative Grounds (Conflicts With Existing Marks)
- The mark is identical or confusingly similar to an earlier registered or pending mark.
- It conflicts with a well-known mark (including foreign well-known marks).
- It may confuse consumers as to the origin of goods/services.
Thailand’s examiners often take a conservative approach, so conducting a clearance search before filing significantly reduces the risk of objection.
Language, Transliteration, and Local Requirements
Thailand accepts trademarks in any language, but several local rules apply:
- Thai transliteration may be recommended
If the English (or other language) name can be phonetically represented in Thai, filing a Thai transliteration can strengthen protection and prevent copycat filings.
- Goods and services must be written in precise, accepted terms
Thailand follows the Nice Classification, but DIP requires very specific and clear item descriptions.
Overly broad wording (e.g., “software”) is often rejected unless clarified.
- Descriptive English wording can trigger objections
For example, marks like “Best Quality”, “Pure Natural”, or “Bangkok Coffee” may be refused unless stylized or combined with distinctive elements.
- If a mark includes Thai characters, spelling must match
Any mistake in Thai script may require submitting a formal amendment to DIP. Such corrections often lead to delays and may generate additional costs, since amendments and re-submissions typically involve both extra attorney time and, in some cases, additional DIP fees.
These nuances make it helpful to work with a verified local representative who understands DIP examination practices and acceptable terminology.
Territoriality and the First-to-File Principle
Thailand strictly follows the first-to-file rule.
This means:
- Rights belong to whoever files first, not who used the mark first.
- Use of a mark without registration provides almost no enforceable rights.
- Foreign businesses expanding into Thailand should file before launching marketing activities, entering distribution agreements, or allowing local partners to begin sales.
Trademark rights in Thailand are territorial, meaning:
- Registration in other countries does not protect you in Thailand.
- A separate application must be filed with DIP.
Early filing is crucial because Thailand does not allow multi-class applications — each class must be filed separately, increasing the importance of early priority.
2.Trademark Registration Process in Thailand: Overview
Step 1 — Preparation: What You Need Before Filing
Before filing a trademark application in Thailand, it is essential to prepare the correct scope of goods and services, determine whether a Thai transliteration or Thai logo version is needed, and gather all supporting documents. Proper preparation significantly reduces the risk of refusal during the DIP (Department of Intellectual Property) examination and makes the filing process predictable and smooth.
Through the iPNOTE platform, the preparation step becomes easier thanks to AI assistance, clear checklists, and support from verified Thai trademark attorneys.
Define Your Goods and Services (Single-Class Applications Only)
Thailand follows the Nice Classification but requires one application per class — multi-class filings are not allowed.
This means:
- you must carefully define your goods/services for each class,
- overly broad descriptions are not accepted,
- DIP examiners expect very precise and specific terminology.
To avoid errors, you can use the AI assistant:
- If you already have a website
Provide the link — the AI scans your products/services and recommends the correct Nice classes and acceptable DIP-approved wording.
- If you do not have a website
Describe your products/services in a few sentences — the AI analyzes the description and proposes proper classes and detailed wording.
This minimizes the risk of objections related to vague or incorrect class descriptions.
Prepare the Required Documents
To avoid delays, prepare the following in advance:
- Trademark file — high-resolution logo (PNG, for example) or word mark specification
- Owner information — full legal name, address, legal entity type
Step 2 — Clearance Search (Trademark Availability Check)
Before filing a trademark in Thailand, it’s essential to check whether the mark is available and distinctive enough to pass DIP examination. Thailand has strict rules on phonetic similarity, Thai transliterations, and descriptive wording, so the quality of the search directly affects your chances of smooth registration.
Option 1 — Instant AI Search on iPNOTE
Using the AI assistant, you can get an immediate preliminary analysis of your trademark.
The AI evaluates obvious risks: identical matches, clear conflicts, basic phonetic issues, and overall distinctiveness.
This helps you quickly understand:
- how high the initial risk level is,
- whether it makes sense to file “as is” or adjust the spelling/classes before paying any fees.
Key benefit: You get a fast, objective, automated assessment without spending money on a lawyer at the early stage.
Start your free check with iPNOTE.
Option 2 — Manual Search by a Thai Trademark Attorney
Thailand is a complex jurisdiction because of:
- multiple possible Thai transliterations for the same English word,
- strict focus on pronunciation similarity,
- DIP’s conservative interpretation of distinctiveness,
- local brands often using mixed Thai/English spellings.
A professional search by a Thai attorney identifies deeper risks such as:
- phonetic equivalents,
- Thai transliteration conflicts,
- conceptual similarity,
- conflicts across related classes,
- DIP-specific terminology issues.
Main benefit: a comprehensive risk evaluation tailored to Thai examination practice.
You can request this manual attorney-led search directly through iPNOTE, choosing from verified Thai trademark attorneys.
How They Differ and Why Both Matter

Best Practice
Most applicants combine both steps:
AI analysis for a quick first impression, followed by a professional Thai attorney review for a complete, risk-free picture.
Together, these two layers significantly reduce the chance of Office Actions, added expenses, and delays during DIP examination.
Step 3 — Filing the Trademark Application
Residents of Thailand and applicants holding a valid Thai residence permit can submit a trademark application directly through the official portal of the Department of Intellectual Property (DIP). (https://www.ipthailand.go.th/en/)
For non-residents, Thai law requires the appointment of a licensed local trademark attorney — filing a trademark application without a Thai representative is not allowed. A qualified representative will submit the application, handle all correspondence with DIP, and manage any corrections or Office Actions.
On the iPNOTE marketplace, you can choose a verified Thai trademark attorney, compare fixed-price offers, and handle the entire filing process in one place with full transparency. The platform’s AI assistant also helps create a correct filing task, prepare documents, and ensure the application aligns with DIP requirements before submission.
This removes language barriers, simplifies coordination, and eliminates the risk of filing errors.
Filing Through iPNOTE: Easy Way to Register in Thailand
For many applicants, especially those unfamiliar with local requirements, or DIP procedures, filing through a platform like iPNOTE removes uncertainty and ensures that every step is completed correctly. The process is transparent, structured, and supported by verified local trademark attorneys.
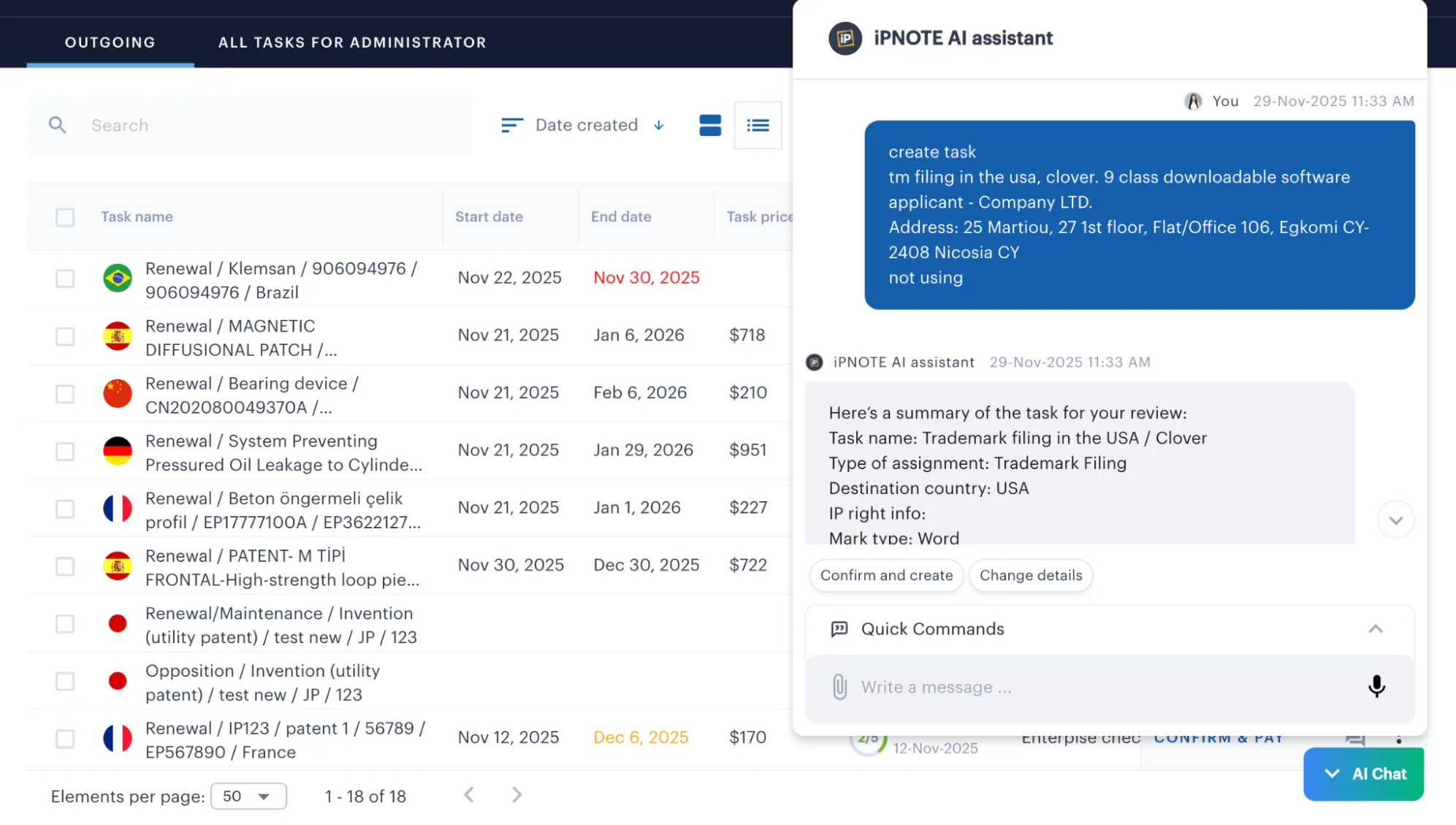
Create a Task for Trademark Registration in Thailand
You begin by creating a task inside the iPNOTE platform.
The integrated AI assistant helps you structure the request correctly:
- estimates the approximate registration cost, taking into account official fees and service charges,
- suggests appropriate Nice classes,
- and ensures the task aligns with DIP requirements.
This eliminates confusion and prevents mistakes at the earliest stage.
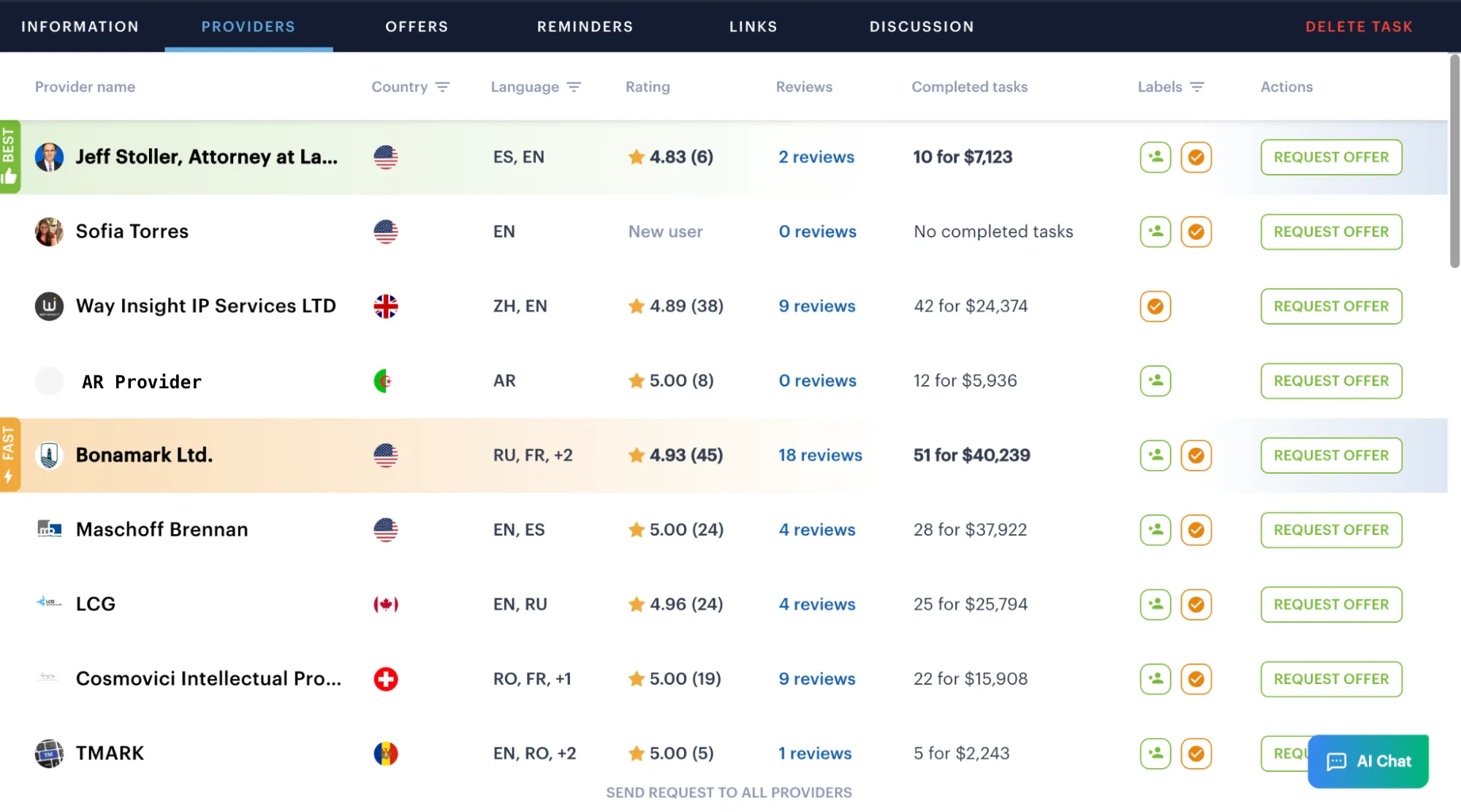
Receive a List of Suitable Providers
Once the task is created, the platform automatically shows a list of verified local trademark attorneys who can handle your filing.
You can:
- select providers manually, based on their profiles,
- ask the AI assistant to choose the most suitable ones,
- or send a request to all providers at once to compare offers.
Every provider has a complete profile with experience, ratings, response times.
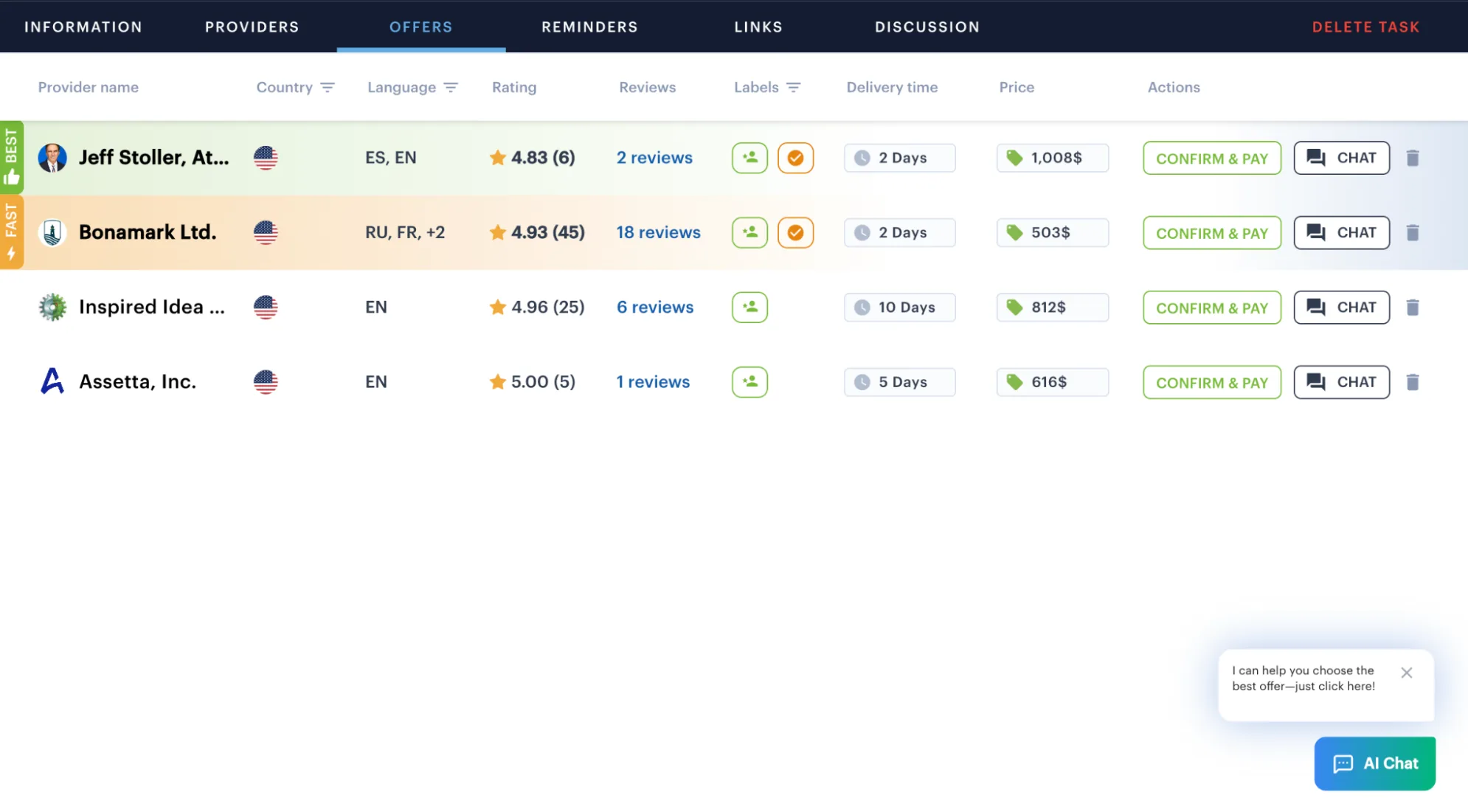
Compare Fixed Offers and Choose the Best Option
Soon after your request, providers will send their offers.
Each offer contains:
- total cost (including official fees, attorney fees, and the platform commission),
- estimated timelines,
- scope of work covered.
You can also open a chat with any provider in the Messages section to clarify details or ask additional questions. This helps you make an informed decision based on clear, measurable factors.
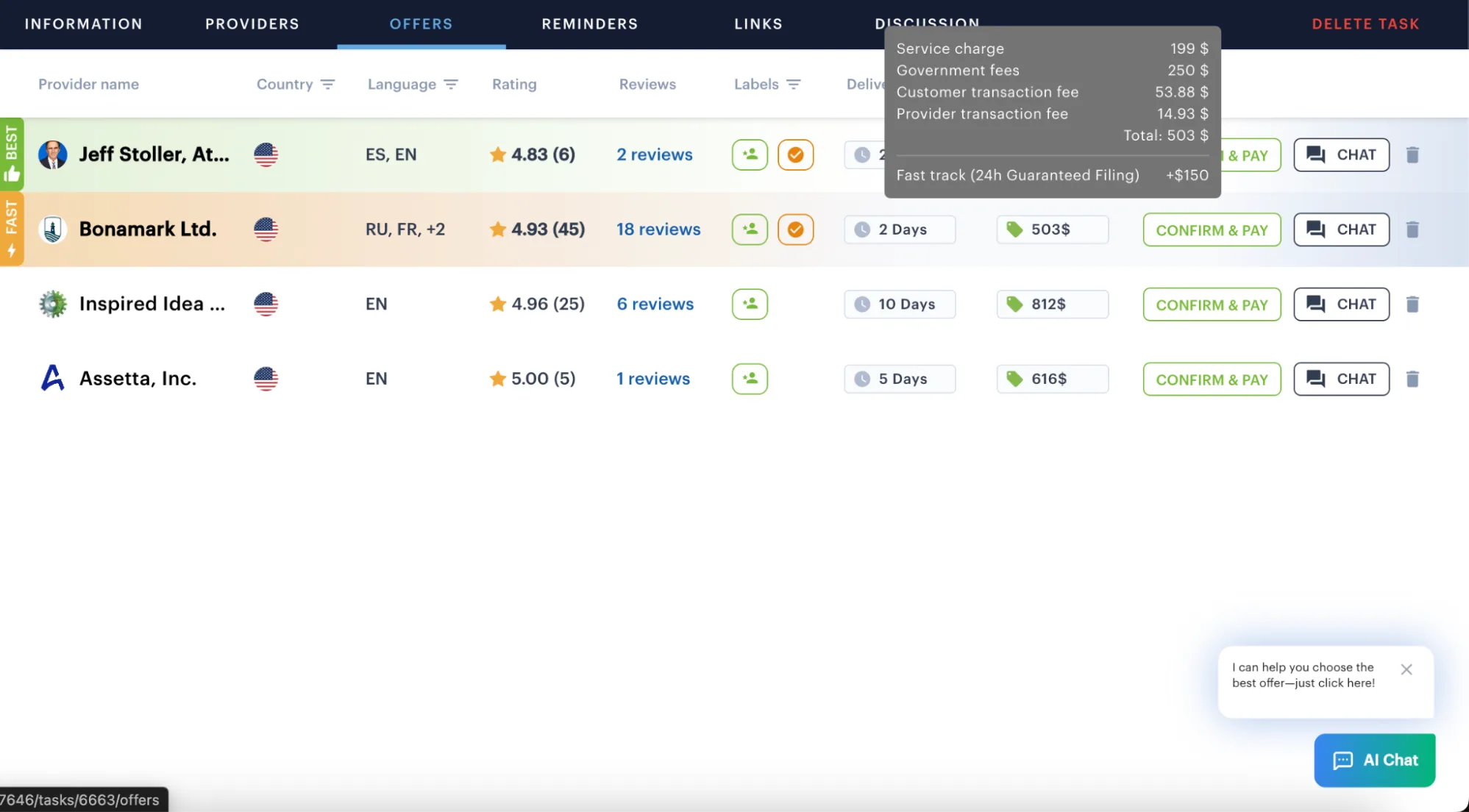
Pay for the Service — All Fees Included
When you choose the best offer, you proceed to payment.
The price displayed includes:
- DIP official fees,
- local representative fees,
- iPNOTE commission.
No hidden charges, no unexpected add-ons later in the process.
The Provider Starts Working Within 24 Hours
After payment, the provider will begin working on your case within one business day.
iPNOTE uses escrow payments, meaning:
- the provider only receives the funds after you approve the final result,
- the platform acts as a neutral guarantor,
- your investment is protected throughout the process.
This eliminates risks and ensures accountability.
Final Review Before Filing
Before submitting the trademark to DIP, your provider sends you the complete filing package for final confirmation:
- the trademark representation,
- transliteration (if applicable),
- selected classes,
- goods/services description,
- owner information,
- priority claim (if any).
You can review everything in one place and request corrections if needed.
Filing and Tracking Your Application Online
Once approved, the provider files the application through DIP.
After submission, on the platform, in your personal account under the IP Rights section appears:
- application stage,
- filing date,
- application number,
- jurisdiction,
- all uploaded documents,
- communication history.
Statuses update automatically, so you always know exactly where your application stands — without waiting for emails or manual updates.
Step 4 — Formal Examination and Substantive Examination
After your trademark application is filed with the Thai Department of Intellectual Property (DIP), it goes through two levels of examination: the formal check and the substantive (absolute/relative) examination. Both stages may result in Office Actions, which are routine procedural communications rather than refusals.
- Formal Examination (Document & Procedural Check)
During the formal review, DIP verifies that your application complies with administrative requirements. Examiners check:
- correctness of all submitted documents,
- accuracy of applicant data (name, address, entity type),
- correct class selection (Thailand = one class per application),
- whether goods/services use DIP-accepted terminology,
- clarity and quality of the trademark file (logo/word mark),
- proper formatting of the Power of Attorney (mandatory for non-residents),
- priority documents (if included, as a copy, the filing date and number of the first (earlier) trademark application filed in another member country, a certified copy of that earlier application (if requested by DIP), a Thai or English translation).
If there is a formal issue, DIP issues a Formal Office Action.
Response deadline: 60 days from the date of the notification.
Extensions:
- Usually one extension is allowed (must be requested before the deadline).
- If no response is filed → the application becomes abandoned (you must refile from scratch).
- Substantive Examination (Distinctiveness, Similarity & Legal Grounds)
If the application passes the formal stage, it moves to substantive examination.
Here, DIP examiners evaluate:
- distinctiveness,
- similarity to earlier registered or pending marks,
- Thai transliteration conflicts,
- similarity in pronunciation,
- conceptual similarity or semantic overlap,
- compliance with the Thai Trademark Act,
- whether the mark contains prohibited elements or descriptive wording.
If concerns arise, DIP issues a Substantive Office Action detailing the examiner’s objections.
Response deadline: 90 days from the date of the substantive Office Action.
Extensions:
- Applicants can request a 30–60 day extension.
- Extensions are not guaranteed — approval depends on the examiner’s discretion and whether the justification is reasonable.
If no response is submitted: The application is refused.
What Happens After DIP Reviews Your Response?
- If DIP accepts the response – Your application proceeds to the Official Gazette publication stage (Step 5).
- If DIP is not satisfied. A refusal is issued. Refusals in Thailand can be appealed, but require legal argumentation and strict procedural steps.
Why Office Actions Are Not a Reason to Panic
Office Actions are normal in Thailand, especially given the strict distinctiveness and transliteration rules.

Step 5 — Publication and Opposition Period
If the Thai Department of Intellectual Property (DIP) approves your trademark during formal and substantive examination, it is published in the Official Gazette. This is a mandatory public stage where your mark becomes visible online, allowing anyone to review the details of your application — the mark itself, the owner’s name, goods and services, and filing information. This step ensures transparency and gives third parties the opportunity to protect their trademark rights before your mark proceeds to registration.
Publication lasts 90 days, during which other trademark owners can check whether your mark conflicts with theirs. If they believe your application is too similar to an existing or pending mark, they may file an opposition.
- If no opposition is filed, the application moves forward to the final registration stage.
- If an opposition is submitted, the process pauses while the dispute is reviewed and resolved.
Oppositions in Thailand follow a structured legal process and must be addressed carefully.
However, when handled by an experienced Thai attorney, they are manageable and often resolved without escalating into long disputes.
Step 6 — Payment of the Registration Fee and Issuance of the Certificate
If no opposition is filed during the 90-day publication period, your application automatically moves into the final registration stage. At this point, the Thai Department of Intellectual Property (DIP) performs one last internal check to confirm that the mark is ready for registration and then issues the final fee request.
Once the payment is completed, DIP prepares the official trademark registration certificate. This typically takes up to 60 days. After the certificate is issued, your IP Rights card inside iPNOTE is updated to include:
- Registration Number
- Certificate issued by DIP (downloadable)
- Issue Date
- Renewal Date
In Thailand, a trademark is valid for 10 years from the filing date, and it must be renewed every 10 years to maintain protection.
3.Budget: What Trademark Registration Costs in Thailand
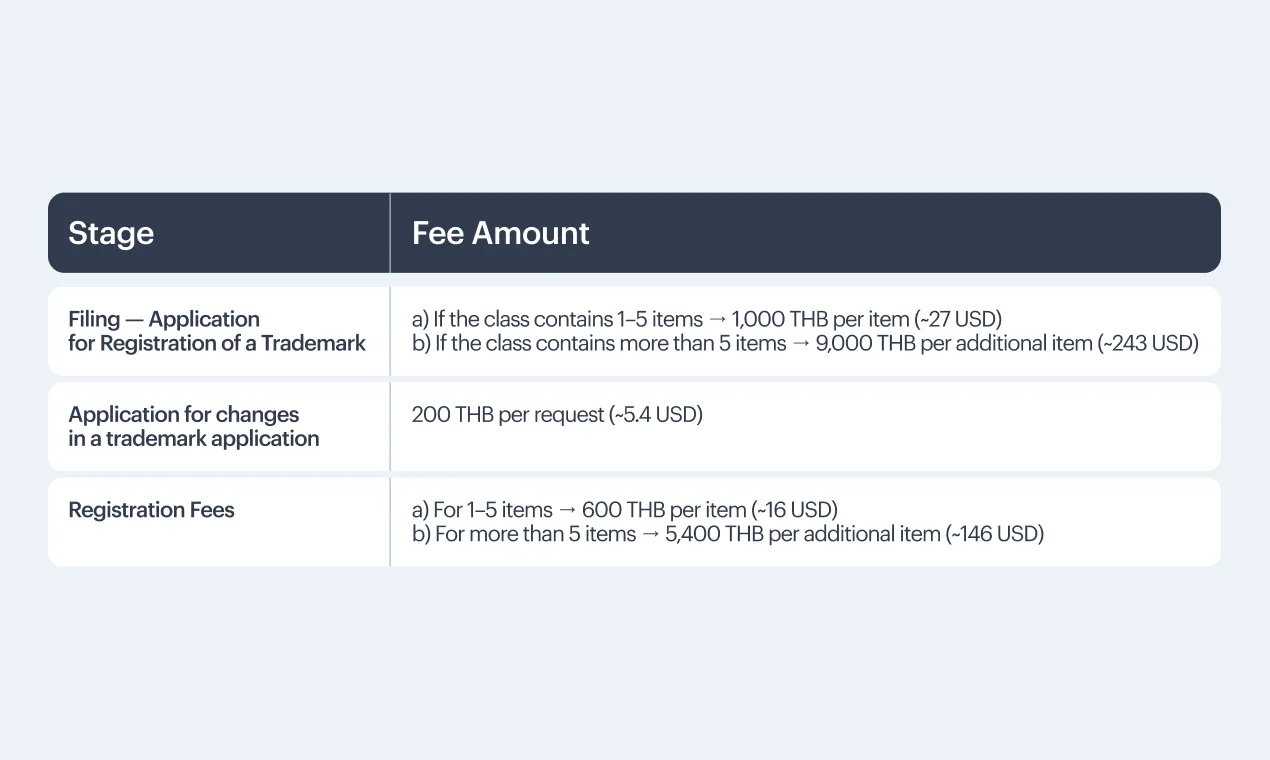
Trademark registration costs in Thailand depend on the number of items listed in each class, local representative fees, and any translation or legalization requirements. Thailand calculates official fees per item.
Government Fees (DIP Official Fees)
Local Representative Fees
Foreign applicants must use a Thai trademark attorney.
Average: ≈ 350 USD per class
This usually includes:
- filing,
- DIP correspondence,
- translation of goods/services wording,
- monitoring deadlines,
- receiving DIP notices,
- submission of corrections.
Translations and Legalizations
May be required if:
- Power of Attorney needs to be in Thai,
- corporate documents require Thai versions,
- goods/services wording must be localized into DIP-approved structure,
- DIP requests clarifications.
How to Save Money
- Minimize the number of items in each class
Example:
10 items → 50,000 THB (~1,350 USD)
5 items → 5,000 THB (~135 USD)
Savings: 45,000 THB (~1,215 USD) per class
- Combine related goods/services into one item
Allowed if:
- wording is clear,
- fits Nice Classification,
- acceptable to DIP.
Example:
Instead of listing: t-shirts, polo shirts, hoodies, sweatshirts, jeans, shorts.
You can combine all into “Clothing”.
Result: 6 items → 1 item
- File the minimum number of classes
Avoid “just in case” classes.
Most businesses can cover their activity in 1–2 classes, not 5–6.
- Conduct a clearance search before filing
Office Actions and refusals lead to:
- delays
- extra attorney fees
- possible re-filing costs
A proper search helps:
- reduce the risk of DIP objections,
- avoid expensive corrections,
- prevent complete re-submission.
- Work with verified Thai attorneys through iPNOTE
This gives you:
-
- direct access to local agents (no law firm markups),
- transparent fixed fees,
- accurate DIP-approved goods/services wording,
- fewer corrections → fewer translation fees,
- escrow protection,
- AI assistance at the preparation stage.
This significantly reduces the chances of errors that trigger extra costs.
4.Timeline: How Long Trademark Registration Takes in Thailand
Trademark registration in Thailand follows a series of predictable steps, but the overall process is significantly longer than in most jurisdictions in Southeast Asia. Even though DIP offers an online filing system, many internal procedures remain manual, which contributes to slowdowns, backlogs, and long waiting periods.
Below is a clear and realistic breakdown of the full timeline — from preparation to certificate issuance — based on current DIP practice.
- Document Preparation
Time: 1–7 business days
This stage depends on how quickly you:
- finalize the goods/services list,
- gather documents,
- prepare the trademark file (logo/word mark),
- issue or translate the Power of Attorney (if required).
On iPNOTE, expected preparation times are visible inside each provider’s offer.
- Filing + Formal Examination (DIP Initial Check)
Time: 1–3 months
Once filed, DIP performs the formal check, reviewing:
- accuracy of applicant details,
- validity of the Power of Attorney for non-residents,
- correctness and clarity of goods/services,
- compliance of wording with DIP-approved terminology,
- proper representation of the mark (image/format),
- correct payment of the filing fee.
- Substantive Examination
Time: 8–16 months
This is the longest and most resource-intensive phase.
DIP examiners evaluate:
- the distinctiveness of the mark,
- whether the mark is descriptive or prohibited,
- conflicts with earlier filed or registered marks,
- Thai transliteration conflicts (a common issue),
- compliance with the Thai Trademark Act.
- Publication in the Official Gazette
Time: 90 days (mandatory)
Once approved by the examiner, the mark is published in the DIP Official Gazette for a strict 90-day opposition period.
During this time:
- the trademark is publicly visible on the DIP website,
- any third party may file an Opposition if they believe the mark infringes their rights.
- Notification to Pay the Registration Fee
Time: 2–6 weeks after the end of the publication period**
Once the 90-day publication window closes, DIP manually:
- checks whether any oppositions were filed on the last day,
- verifies that all data is correct,
- ensures procedural timelines were followed.
After this internal review, DIP issues the Notification of Registration Fee Payment.
- Payment of the Registration Fee & Certificate Issuance
Time after payment: 4–8 weeks
After the registration fee is paid:
- DIP processes the file,
- prepares the official certificate.
The official Trademark Registration Certificate is issued within 4–8 weeks, depending on DIP workload.
Total Registration Time in Thailand
Typical duration: 12–24 months
With Office Actions: up to 30 months
Thailand is known for having one of the longest trademark examination periods in the region due to:
-
- manual internal processes at DIP,
- high application volume,
- limited examination staff,
- growing popularity of Thailand as a trademark jurisdiction,
- slow post-publication workflows (manual status updates, manual fee notifications, manual certificate processing).
This makes early filing critical — and working with a professional local representative helps avoid delays.

5.Conclusion and Next Steps
Trademark registration in Thailand is a multi-stage process with strict rules, long examination periods, and mandatory use of a local representative. When handled carefully, from preparing goods and services, checking availability, and filing correctly, to managing Office Actions, publication, and final registration, the entire journey becomes predictable and manageable.
Working with verified local experts allows you to avoid delays, reduce costs, and keep full control over deadlines and requirements. To save time and money, it is essential to rely on a trusted partner who understands the Thai system and can manage each step professionally.
With iPNOTE, you can compare offers from licensed Thai attorneys, track every stage online, and receive full transparency from filing to certificate.
Protect your brand in Thailand with confidence — start your trademark registration on iPNOTE today.