“The cost of patenting depends on many factors — including the country, type of invention, scope of work, choice of service providers, and ongoing maintenance fees.”
If you’re considering patenting your invention, one of the first questions you’ll ask is: How much will it cost? The honest answer is: It depends.
There is no one-size-fits-all price for patent registration. The total cost can vary significantly based on your strategy, the number of countries where you want protection, the complexity of your invention, and even the service providers you choose. In this guide, we break down what goes into the cost of a patent, show examples by country, and explain how to estimate your budget accurately.
Content
1. Why There Is No Universal Patent Price
2. Main Components of Patent Costs
3. Example Cost Ranges by Country
4. Why «From…To» Is the Most Honest Answer
5. What Drives Patent Costs Up or Down?
6. Where You Can Save and Where You Shouldn’t
7. Conclusion: Plan Smart and Estimate Precisely
Why There Is No Universal Patent Price
The cost of a patent isn’t just about filing a form and getting a certificate. It’s a multi-stage process involving legal, technical, and sometimes linguistic work. A simple invention filed in one country may cost only a few thousand dollars. A more complex invention, protected internationally, may cost tens of thousands over its lifetime.
- Country or region of filing
- Type of patent (utility, design, provisional, etc.)
- Number of claims or independent claims
- Attorney and agent fees
- Number of countries for protection
- Translation and documentation needs
- Responses to examination and legal office actions
- Ongoing maintenance (annuities or renewal fees)
Let’s explore each component in more detail.
Main Components of Patent Costs
1. Government Fees
Every country’s patent office charges official fees for:
- Filing the application
- Requesting examination
- Publishing the application
- Granting the patent
- Renewals or annuities over the life of the patent
These fees are typically fixed but vary by country, and may offer discounts for individuals, universities, or small businesses.
2. Patent Attorney or Agent Fees
Unless you’re a patent expert, you’ll need help:
- Drafting the application
- Filing it correctly
- Responding to legal or technical objections
- Managing communication with patent offices
Attorney fees vary based on region and service scope. Drafting a well-structured patent can be a significant portion of the total cost — but also a critical investment.
3. Translation Costs
For international filings, accurate translations into the local language are required. This adds significantly to the budget — especially for countries like Japan, China, and Korea, where high-quality legal translation is essential.
4. Maintenance Costs
Once granted, patents are not “set and forget”. You must pay annual or periodic renewal fees to keep the patent active. If you forget or delay, the patent may lapse or become unenforceable.
5. Additional Costs
During prosecution, other costs may arise:
- Office Actions: Examiner responses and amendments
- Drawings and illustrations: Required in formal format
- Legal clarifications and appeals
- Oppositions and litigation (if disputes arise)
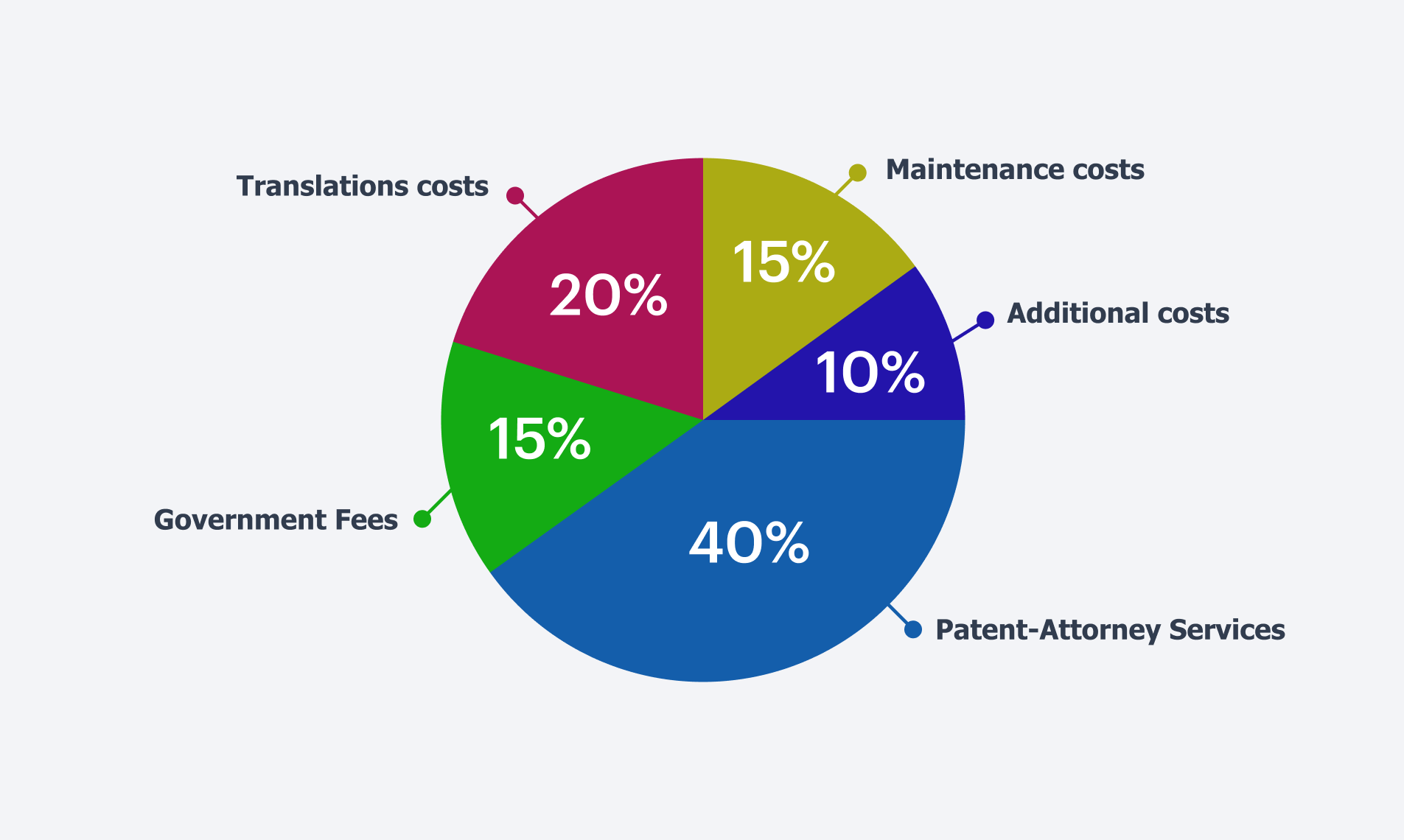
Average budget allocation for a standard patent strategy, 2025
Example Cost Ranges by Country
Here’s a rough overview of the typical cost ranges in key patent jurisdictions, including both official and professional service fees:
United States (USPTO)
- Total cost: $5,000-$15,000+
- Filing + examination fees: ~$400-$1,200
- Drafting and attorney services: $3,000-$10,000
- Maintenance fees (3.5, 7.5, and 11.5 years): ~$8,000 total
- Notes: Strong IP enforcement; cost varies based on number of claims
Europe (EPO + Validation in Member States)
- Total cost: €6,000-€20,000+
- Filing & examination: €4,000-€6,000
- Validation (translation + local agents): €3,000-€10,000
- Notes: Requires validation in each country; adds cost
China (CNIPA)
- Total cost: $4,000-$10,000
- Government fees: low (~$200-$400)
- Drafting and filing: $2,000-$6,000
- Translation (if needed): $1,000+
- Notes: Fast-growing IP market; strong local protection
Japan (JPO)
- Total cost: $7,000-$15,000
- Official fees: ~$1,000
- Translation + legal review: $3,000-$6,000
- Notes: Complex system, detailed examination
South Korea (KIPO)
- Total cost: $5,000-$12,000
- Official and legal fees: moderate
- Efficient procedures and growing regional importance
- Total cost: $2,500-$6,000
- Filing and examination: low to moderate
- Attorney services: $1,500-$4,000
- Notes: Cost-effective for emerging markets
Why «From…To» Is the Most Honest Answer
Pricing a patent is not like buying a product off the shelf. Even within a single jurisdiction like the U.S., costs vary depending on:
- Technical field and complexity
- Length and clarity of the description
- Number of claims and drawings
- Responses required during examination
- Your choice of agent or law firm
Therefore, ranges (e.g., $5,000-$15,000) reflect realistic scenarios, not vague estimates. Instead of guessing or Googling endlessly, try our AI chat to view your patent cost estimate now.
What Drives Patent Costs Up or Down?
Here’s what has the biggest influence on your final patent budget:
Number of Countries
- National vs. Regional (e.g., EPO) vs. International (PCT)
- More countries = More filings, translations, renewals
Invention Complexity
- Simple mechanical idea = cheaper to describe
- AI, pharma, or semiconductor = complex, more attorney time
- More jurisdictions = more translations + legal review
- Legal terminology accuracy is crucial for enforcement
Legal Events
- Examiner objections (Office Actions)
- Oppositions from competitors
- Enforcement and litigation, if needed
Where You Can Save and Where You Shouldn’t
Save smart:
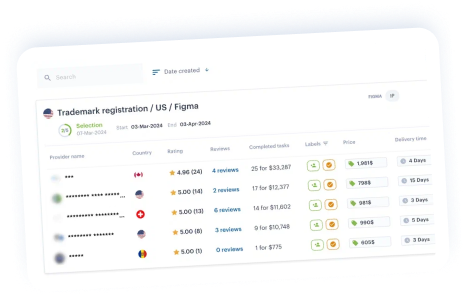
- Use a local provider from iPNOTE marketplace to find the best fit
- Focus on strategic countries for commercial value
- Start with a provisional patent if uncertain
Avoid mistakes:
- Overpaying for unnecessary “package deals”
- Filing in countries where you’ll never commercialize
- Ignoring future costs (renewals, disputes)
Conclusion: Plan Smart and Estimate Precisely
Patents are powerful tools — but they aren’t cheap. Instead of making decisions blindly, you can use our free tool to get accurate, obligation-free cost estimates for your invention in minutes.
Try it now: Post a task -> Get real offers -> Compare providers -> Choose the best fit for your budget and goals.